How to Choose the Right Life Insurance Policy: A Comprehensive Guide
Life insurance plays a crucial role in securing your financial future, but choosing the right policy can be a daunting task. With so many options and features available, it’s important to understand the basics of life insurance, what different policies offer, and how they fit into your financial plan. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the ins and outs of life insurance, from understanding policy types to deciding on the best coverage for your specific needs.
II. Types of Life Insurance Policies
Choosing the right life insurance policy starts with knowing the different types available. Each policy serves a unique purpose and is designed to meet specific needs.
1. Term Life Insurance
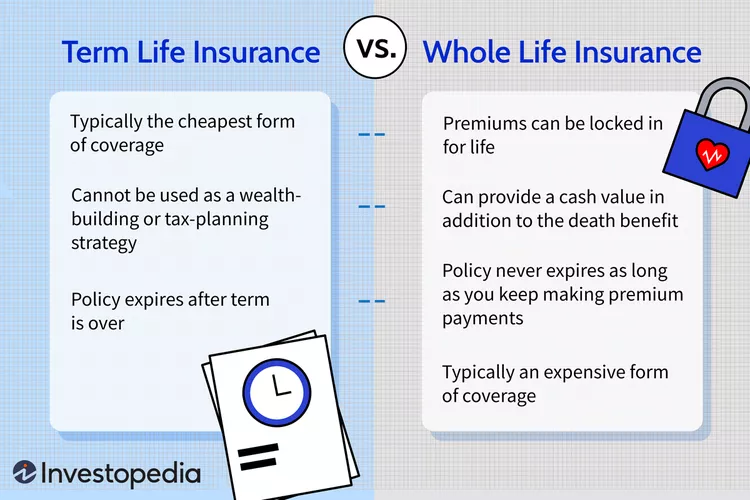
Term life insurance provides coverage for a specific period, typically 10, 20, or 30 years. It is one of the simplest and most affordable forms of life insurance, offering a straightforward death benefit if the policyholder dies within the term.
- Features of Term Life Insurance
Term life insurance has no cash value, and the policyholder must renew or purchase new coverage once the term expires. - Pros and Cons of Term Life Insurance
Pros: Lower premiums, simple structure
Cons: No cash value, coverage ends after the term
2. Whole Life Insurance
Whole life insurance offers permanent coverage and includes a savings component known as cash value.
- Features of Whole Life Insurance
Whole life insurance guarantees a death benefit and builds cash value over time. - Pros and Cons of Whole Life Insurance
Pros: Lifelong coverage, cash value growth
Cons: Higher premiums, more complex structure
(Continue with rest of the article structure)
4o
You said:
Continue
ChatGPT said:
ChatGPT
2. Whole Life Insurance (Continued)
Whole life insurance provides the certainty of lifelong coverage, but it also comes with higher premiums than term policies. The cash value grows at a guaranteed rate, and policyholders can borrow against this amount or use it for retirement income.
- Pros and Cons of Whole Life Insurance
Pros:- Lifelong Protection: You are covered for your entire life as long as premiums are paid.
- Cash Value Growth: It builds cash value, which can be accessed during your lifetime.
- Tax Advantages: Cash value grows on a tax-deferred basis.
- High Premiums: Whole life policies are significantly more expensive than term policies.
- Complexity: It’s harder to understand due to the savings and investment components.
3. Universal Life Insurance
Universal life insurance is another form of permanent life insurance that combines a death benefit with a savings element. However, it offers more flexibility in terms of premium payments and death benefits compared to whole life insurance.
- Features of Universal Life Insurance
Policyholders can adjust their premiums and death benefits within certain limits. This policy also accrues cash value based on market interest rates or investment returns, depending on the type of universal life policy. - Pros and Cons of Universal Life Insurance
Pros:- Flexible Premiums and Death Benefit: You can adjust the policy to fit changing financial situations.
- Cash Value Growth Potential: Growth is based on market rates, which could lead to higher returns than whole life insurance.
- Complexity: Policyholders need to monitor their premiums and cash value carefully.
- Market Risk: Cash value growth is tied to market performance, which can fluctuate.
4. Variable Life Insurance
Variable life insurance is a permanent policy that allows the policyholder to invest the cash value in various investment options, such as stocks, bonds, or mutual funds.
- Features of Variable Life Insurance
The death benefit and cash value vary based on the performance of the investments chosen. While this offers higher growth potential, it also comes with more risk. - Pros and Cons of Variable Life Insurance
Pros:- Investment Options: Potential for significant cash value growth based on market performance.
- Flexible Death Benefit: You can increase or decrease the death benefit based on investment performance and needs.
- Risky: Your policy’s value can fluctuate with the market.
- Higher Fees: Management of investment accounts can result in additional costs.
5. Final Expense Life Insurance
Final expense life insurance is a type of whole life insurance designed to cover funeral and burial costs. The coverage amounts are typically lower, usually ranging from $5,000 to $25,000.
- Features of Final Expense Life Insurance
This policy is easy to qualify for, with many not requiring medical exams. It’s often marketed to seniors looking to ensure that their end-of-life expenses are covered. - Pros and Cons of Final Expense Life Insurance
Pros:- Easy to Qualify: Minimal medical underwriting is required.
- Low Premiums for Seniors: Designed specifically for end-of-life expenses.
- Low Coverage: The death benefit is limited to covering funeral costs and small debts.
III. Understanding Life Insurance Terms
Choosing a policy requires familiarity with specific terms to ensure you understand the coverage you’re buying.
1. Premiums
The amount you pay to maintain your life insurance policy. This can be a fixed monthly or annual payment, or it can vary in flexible policies like universal life insurance.
2. Death Benefit
The amount paid to your beneficiaries when you pass away. The death benefit can be a fixed amount or vary based on policy performance.
3. Cash Value
The savings or investment portion of a permanent life insurance policy. This value grows over time and can be accessed while you are still alive.
4. Riders and Endorsements
Riders are additional benefits or coverage options that can be added to a base policy, such as critical illness coverage or accidental death benefits.
5. Surrender Value
If you decide to cancel your permanent life insurance policy, the surrender value is the amount you will receive after any fees are deducted.
6. Beneficiaries
The individuals or entities that will receive the death benefit of the policy upon the insured’s death.
7. Underwriting Process
The process by which insurers assess the risk of insuring you, which typically involves evaluating your health, lifestyle, and other factors.
IV. Key Considerations When Choosing a Policy
Selecting the right life insurance policy involves several key considerations that should be tailored to your unique circumstances.
1. Determining Your Coverage Needs
Think about the expenses that would need to be covered if you were to pass away. This might include replacing your income, paying off debt, or covering education costs for your children.
2. Calculating How Much Life Insurance You Need
A general rule of thumb is to aim for a death benefit that’s 10-12 times your annual income, but specific needs vary depending on your family’s financial situation.
3. Life Stage Considerations
Your age and life stage heavily influence what type of life insurance is appropriate. A young, single individual may need less coverage than someone with a family and mortgage.
4. Income Replacement Needs
If you’re the primary earner in your household, your policy should ensure that your family can maintain their standard of living without your income.
5. Assessing Financial Obligations
Consider all debts, such as mortgages, personal loans, and credit cards, and factor them into your coverage needs.
6. Term vs. Permanent Life Insurance: Which is Best?
Evaluate whether you need coverage for a specific period (term insurance) or lifelong protection (permanent insurance). Term is ideal for temporary needs, while permanent is better for long-term planning.
7. Impact of Health and Lifestyle on Premiums
Your health, lifestyle choices, and habits (like smoking) will impact the premiums you pay. It’s important to undergo a medical exam to receive the most accurate quote.
8. Policy Duration and Flexibility
Ensure that your policy’s duration aligns with your needs, and consider policies that offer flexible premium and coverage options.
V. Benefits of Life Insurance
Life insurance offers a multitude of benefits beyond just the death benefit.
1. Financial Protection for Loved Ones
The primary benefit is that life insurance provides your loved ones with financial security in the event of your death.
2. Income Replacement
Life insurance can replace lost income, ensuring that your family can meet their day-to-day expenses.
3. Estate Planning
Life insurance can play an essential role in estate planning by helping to cover estate taxes, ensuring that your heirs are not burdened with financial liabilities.
4. Tax Benefits of Life Insurance
The death benefit paid out from life insurance is generally tax-free, providing financial peace of mind to your beneficiaries.
5. Building Cash Value with Permanent Insurance
With permanent life insurance policies, cash value accumulates over time and can be used as an additional source of income in retirement.